Identifiers play an essential role in the success of a DPP. This is because it uniquely identifies each product on the market and provides the associated information needed to effectively manage the entire lifecycle and ensure regulatory compliance.
The ESPR stipulates in Article 8 paragraph 3 that a GTIN (Global Trade Identification Number) in accordance with the ISO/IEC 15459 standard or an equivalent identifier for products or parts thereof must be used for product identification. The newCPR also specifies the use of a GTIN or another globally established standard for unique product identification.
In this white paper, reference is made below to the use of the GTIN. This ensures consistency and clear identifiability across different platforms and stakeholders. GTINs are typically used for retail products, outer packaging or entire pallets and are essential as they make each product version clearly identifiable. GTINs can also be supplemented with lot numbers or serial numbers to specify the level of identification and improve traceability.
For “make to order” or “engineer to order” products, serialized identifications via non-speaking serial numbers, so-called Global Individual Asset Identifiers (GIAI), are also permitted.
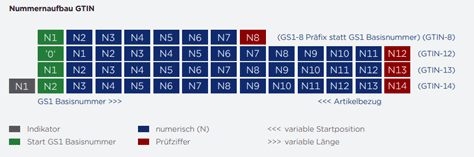
There are four different GTIN formats. The basic format has 14 digits, whereby the last digit is always a check digit. If the basic format is shorter than 14 digits, it is preceded by leading zeros.
Copyright
This document is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License as Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike.
Further information is available at: Creative Commons

