The Common Data Environment (collaboration platform) is an essential basis for handling collaboration in the course of project implementation. A CDE is usually provided by the client in projects. In an ideal scenario, a client with internal BIM project expertise processes its entire portfolio on a CDE, thereby reducing set-up costs while benefiting from the advantages of centralized data storage and uniform structuring.
CDE is generally understood to mean a web-based platform for collaboration between the entire planning team – this enables collaboration between different applications. Integrated collaboration platforms are used to carry out collaboration within a specialist discipline – these enable collaboration within a specific application and offer options such as real-time collaboration and joint work down to element level or even feature level.
Development history
The British BIM standard PAS 1192 described the function and structure of a CDE for the first time in 2007. Collaboration on a file basis was assumed – as can be realized with simple file sharing platforms (e.g. Nextcloud). The status of a file was declared via its assignment to a folder(Work In Progress, Shared, Puplished, Archived).
ISO 19650 defines the CDE as the central component of a PIM(Project Information Model), in which all project information is collected, exchanged and transferred to the AIM(Asset Information Model) for project completion. The underlying structure was adopted from PAS 1192 – as this forms the basis of the ISO 19650 series.
Currently available CDEs offer a much more complex range of functions with the integration of project-related (e-mail) communication, file/plan exchange, model/comment exchange and the viewer function. The implementation of the original concept of PAS 1192 is nowadays often realized via status information and file versioning in order to enable interaction with workflow functionalities.
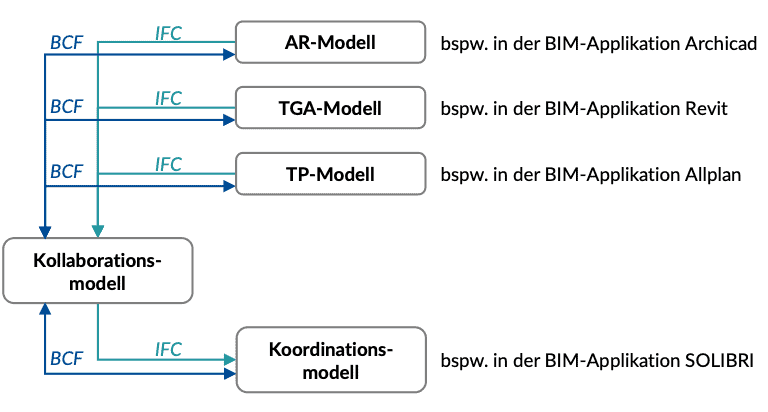
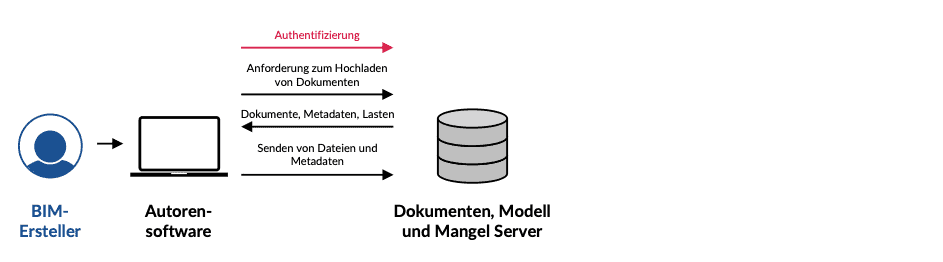
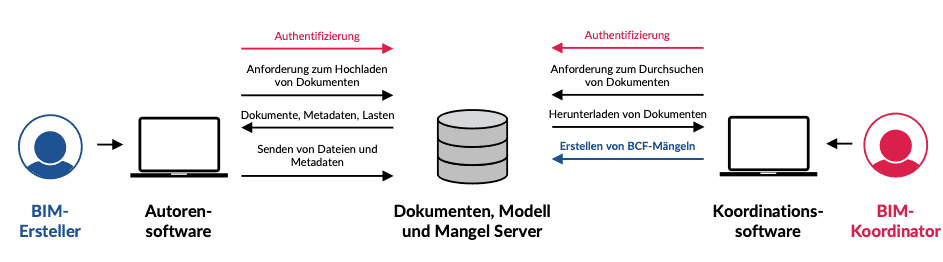
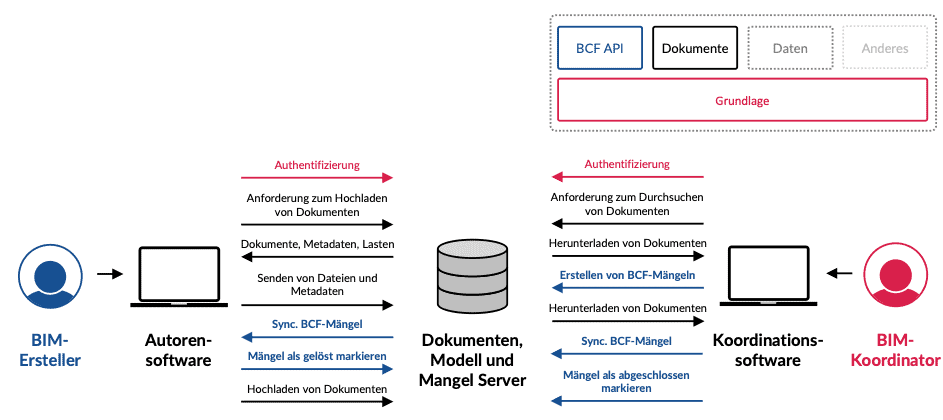
The weak point of the CDE in practice to date is the high effort involved in providing information. Until now, the parties involved have had to upload documents, plans, models (IFC) and model comments (BCF) to the CDE more or less manually and declare them accordingly. This sometimes (product-dependent) complex work is time-consuming and error-prone. The following figures describe the typical effort involved in providing (Fig. 3.44) model information on the CDE and in checking and providing the test results (Fig. 3.45).
These disadvantages are to be eliminated in future by using a web service-based connection of the applications to the CDE – this technology is currently being established under the name openCDE.
The exchange is no longer processed at file level, but on the basis of data bank-based web services. Manual declaration is no longer necessary; only changes are transferred. This optimizes the data volume and therefore the transmission time. Fig. 3.47 describes the reduced effort involved in model-based communication.
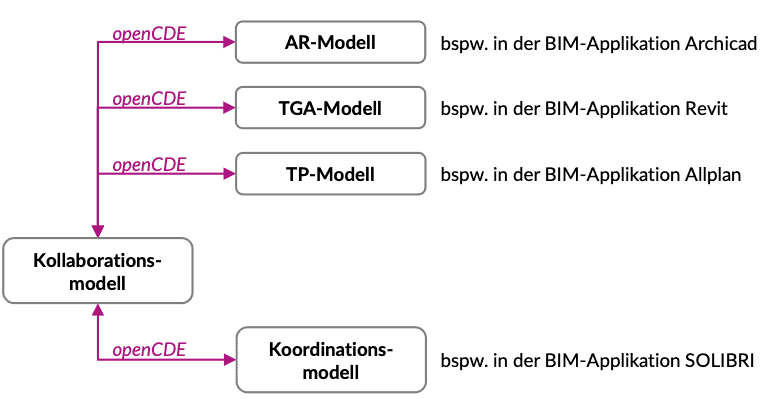
This technology has already been used in the BIMcollab communication platform, which connects BIM applications to the BIMcollab server using special add-ons. With openCDE , this technology can now be used for all CDEs.
Objective of a CDE
The objective of a CDE is:
- The creation of a unique data environment for a project and its project team or a data environment for a complete portfolio of different projects and their respective project teams;
Advantage: rapid availability of information, clear retrievability of information, centralized evaluation of all projects (for portfolio); - Ensuring the necessary data security through encrypted data transmission, user authentication, multi-client capability, role-based user concept;
Advantage: Ensuring the necessary discretion regarding sensitive information, ensuring compliance with legal requirements; - the consistent and uniform structuring of all project information (also across projects);
Advantage: easier project management due to easier evaluation of the project status, easier comparability of project information; - the uniformly controlled implementation of project processes (also across projects);
Advantage: simplified project management due to predefined processes with clear responsibilities and comprehensible communication; - Fast and precise survey of the project status using predefined parameters (also across projects);
Advantage: simplified project management; - easier identification of relevant project content/processes for archiving or compact transfer of relevant project content/processes for archiving at the end of the project, and
- Facilitated identification of relevant project content/processes for operational management or compact transfer of relevant project content/processes to operational management or AIM at relevant times.
Criteria for CDE
A CDE is a central data room for all project information. Its operation is therefore subject to data protection criteria and the warranty claims to be taken into account. The CDE is often provided on the provider’s hardware, as clients do not have access to the necessary technical performance and security in their own IT structures. In such cases, the client must check both the data protection conformity of the provider’s service and its conformity with the required warranty claims regarding availability, reliability, physical access, incompatibility of dependency on third parties, etc. Such requirements often conflict with the client’s own specifications. Such requirements are often at odds with currently advertised cloud offerings. The advantages and disadvantages must be carefully examined here.
Publication from Eichler, C.C., Schranz, Ch., Krischmann, T., Urban, H., Hopferwieser, M., Fischer, S.: BIMcertHandbuch- Grundlagenwissen openBIM. Issue 2024. Mironde-Verlag, Niederfrohna, 2024. DOI: 10.34726/5384
URL: https://repositum.tuwien.at/bitstream/20.500.12708/192612/3/Eichler-2024-BIMcert %20Handbuch%20basic-knowledge%20openBIM-vor.pdf
Status: 23.01.2024
